There are three types of TOS; Neurogenic, Arterial and Venous.
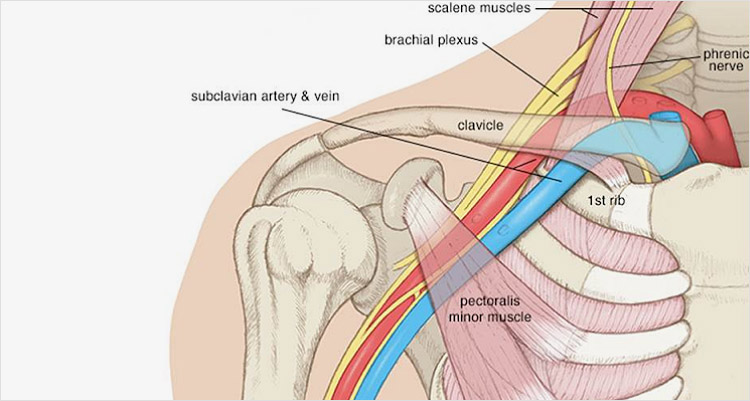
Anatomy
The brachial plexus and subclavian artery course through a triangle as they go to the arm from the chest. The triangle is bounded by muscles at the front and back with the first rib as the base.
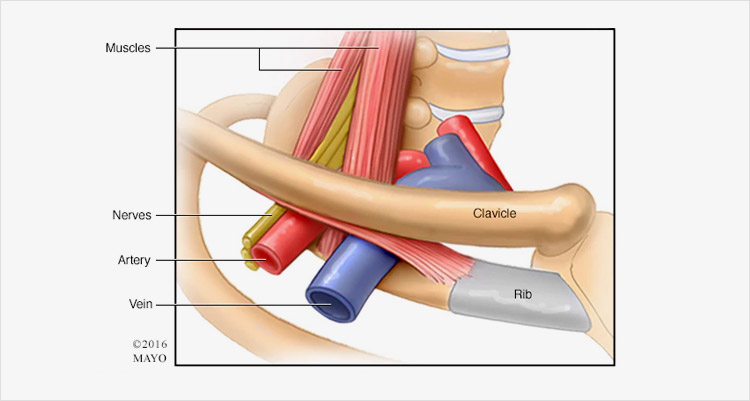
Nerve and arterial symptoms are caused by the space being reduced especially during elevation and rotation of the arm (movements made when brushing your hair or hanging washing on the line). If the symptoms become troublesome firstly physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles is advocated. If this fails consideration is given to decompression of the thoracic outlet by surgical needs.
Venous symptoms usually present with a painful blue swollen arm due to thrombosis (blood clot blockage) of the subclavian vein. Veins along the affected arm usually distend and there may be new collaterals prominent veins that naturally form to bypass the blockage.






